
Embark on a journey to unravel the essence of asset allocation, its significance in investment, and how it shapes risk and return.
Delve into the realm of asset allocation and discover its impact on your investment strategy.
What is Asset Allocation?
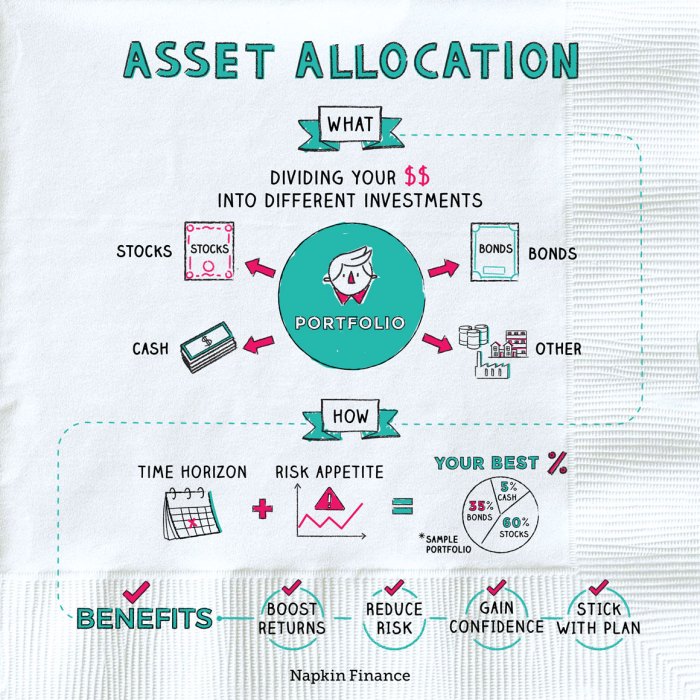
Asset allocation is the strategy of dividing your investment portfolio among different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and cash equivalents, to achieve a specific risk and return objective.
Importance of Asset Allocation in a Portfolio
Asset allocation is crucial in a portfolio as it helps investors diversify their investments, reduce risk, and optimize returns over the long term.
How Asset Allocation Helps Manage Risk and Return in Investments
- Asset allocation spreads investments across different asset classes, reducing the impact of volatility in any single asset.
- By diversifying, investors can mitigate the risk of losing money due to fluctuations in a specific market or industry.
-
Asset allocation allows investors to balance the trade-off between risk and return based on their financial goals and risk tolerance.
- It helps in achieving a more stable and consistent performance by adjusting the allocation as market conditions change.
Asset Management

Asset management plays a crucial role in optimizing investment portfolios by making strategic decisions on how to allocate resources across different asset classes. While asset allocation focuses on the broader distribution of assets, asset management involves the day-to-day monitoring, buying, selling, and adjusting of these assets to meet specific investment goals.
Differentiate between asset management and asset allocation
Asset management involves the active management of assets within a portfolio, focusing on maximizing returns and minimizing risks. Asset managers make decisions on which securities to buy or sell based on market conditions, economic outlook, and individual investor preferences. On the other hand, asset allocation refers to the strategic distribution of assets across various classes such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities to achieve a balance between risk and return.
Explore the role of asset management in optimizing investment portfolios
- Asset managers use various strategies to enhance portfolio performance, such as diversification, market timing, and active trading.
- They conduct in-depth research and analysis to identify investment opportunities and adjust the portfolio accordingly.
- Asset managers also consider factors like liquidity needs, risk tolerance, and investment time horizon when making decisions.
Provide examples of asset management strategies used in the industry
- Active Management: Involves frequent buying and selling of securities in an attempt to outperform the market.
- Passive Management: Focuses on tracking a specific market index, such as the S&P 500, with minimal trading to replicate market performance.
- Value Investing: Seeks to identify undervalued securities with growth potential for long-term capital appreciation.
- Growth Investing: Targets stocks of companies expected to experience above-average growth in earnings and revenues.
In conclusion, asset allocation stands as a cornerstone in navigating the complexities of investments, offering a strategic approach to balancing risk and return.
Questions and Answers
What factors should be considered when defining asset allocation?
Asset allocation considers factors like risk tolerance, investment goals, time horizon, and market conditions.
How does asset allocation differ from asset management?
Asset allocation focuses on distributing investments across different asset classes, while asset management involves overseeing and making decisions about those investments.





