
As Target-date asset allocation funds take the spotlight, this introduction invites readers into a realm of financial expertise, ensuring an engaging and informative exploration of the topic.
Exploring the concept of target-date asset allocation funds and their impact on investment portfolios sets the stage for a comprehensive understanding of this strategic financial tool.
Target-date asset allocation funds
Target-date asset allocation funds, also known as target-date funds or lifecycle funds, are investment vehicles that automatically adjust their asset allocation over time based on the investor’s target retirement date. These funds typically consist of a mix of stocks, bonds, and other assets that are rebalanced periodically to become more conservative as the investor approaches retirement.
Purpose of target-date funds in investment portfolios
Target-date funds aim to simplify the investment process for individuals by providing a diversified portfolio that gradually becomes more conservative as the investor approaches retirement. This helps reduce the risk of significant losses as retirement nears, as the fund automatically adjusts the asset allocation to align with the investor’s changing risk tolerance and time horizon.
Automatic adjustment of asset allocation
Target-date funds automatically adjust their asset allocation by shifting from a higher percentage of stocks to a higher percentage of bonds and other fixed-income securities as the target retirement date approaches. This gradual shift aims to reduce the overall risk exposure of the fund and protect the investor’s capital from market volatility as retirement nears.
Examples of popular target-date asset allocation funds
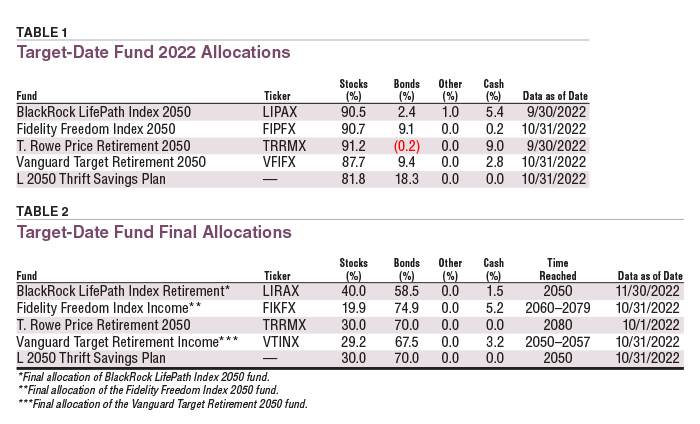
- Vanguard Target Retirement Funds: Vanguard offers a series of target-date funds with target retirement dates ranging from 2015 to 2065, each designed to meet the needs of investors with different retirement timelines.
- Fidelity Freedom Funds: Fidelity’s lineup of target-date funds includes options with target retirement dates in five-year increments, offering investors a range of choices based on their retirement goals and risk tolerance.
- T. Rowe Price Retirement Funds: T. Rowe Price’s target-date funds are designed to provide a diversified portfolio that automatically adjusts its asset allocation over time, with target retirement dates available in five-year intervals.
Asset management

Asset management in the context of finance refers to the professional management of investments and other assets on behalf of clients. This involves making decisions regarding buying, selling, and holding various securities to achieve specific financial objectives.
Asset management companies play a crucial role in managing investment portfolios for individuals, institutions, and other entities. These companies employ financial professionals who analyze market trends, assess risk levels, and make strategic investment decisions to help clients achieve their financial goals.
The Importance of Asset Management
Asset management is essential for maximizing returns while minimizing risks. By diversifying investments across various asset classes, sectors, and regions, asset managers can reduce the impact of market volatility on a portfolio. Additionally, asset management involves continuous monitoring and adjustment of investments to adapt to changing market conditions and client needs.
Active vs. Passive Asset Management Strategies
Active asset management involves frequent trading and portfolio adjustments in an attempt to outperform the market. Asset managers actively research and analyze investments to identify opportunities for profit. On the other hand, passive asset management, also known as index investing, aims to match the performance of a specific market index by holding a diversified portfolio of securities that mirror the index composition.
Asset Allocation
Asset allocation is the process of dividing an investment portfolio among different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and cash equivalents. This strategy is crucial in investment planning as it helps investors manage risk, maximize returns, and achieve their financial goals.
Principles of Asset Allocation
Asset allocation principles are based on an individual’s risk tolerance and investment goals. By diversifying investments across various asset classes, investors can reduce the impact of market volatility and strive for a balanced portfolio that aligns with their objectives.
- Investors with a higher risk tolerance may allocate a larger portion of their portfolio to equities, which have the potential for higher returns but also come with greater volatility.
- On the other hand, investors with a lower risk tolerance may prefer a more conservative approach, allocating a larger portion to fixed-income securities like bonds, which offer stability but lower returns.
- By balancing different asset classes based on risk and return characteristics, investors can create a well-rounded portfolio that suits their individual financial needs.
Asset Classes in Diversified Allocation
Diversified asset allocation strategies typically include the following asset classes:
- Equities: Represent ownership in a company and offer potential for long-term capital growth.
- Bonds: Debt securities issued by governments or corporations, providing income through interest payments.
- Cash Equivalents: Highly liquid and low-risk investments like money market funds, offering stability and immediate access to funds.
- Real Estate: Investments in physical properties or real estate investment trusts (REITs) for diversification and potential income.
Asset Allocation Models
Various asset allocation models, such as the traditional 60/40 (60% stocks, 40% bonds) or target-date funds, aim to achieve specific financial objectives based on an investor’s time horizon and risk tolerance.
- Target-Date Funds: These funds automatically adjust the asset allocation mix over time, becoming more conservative as the target retirement date approaches. They offer a convenient way for investors to maintain a diversified portfolio without constant monitoring.
- Dynamic Asset Allocation: This strategy involves actively adjusting the asset mix based on market conditions, economic outlook, and other factors to capitalize on opportunities and manage risk effectively.
In conclusion, target-date asset allocation funds offer a structured approach to achieving financial goals, providing investors with a well-defined path towards retirement success. This discussion highlights the importance of strategic asset management and allocation in securing a stable financial future.
Questions Often Asked
What are the key features of target-date asset allocation funds?
Target-date funds automatically adjust asset allocation based on the investor’s retirement date, providing a hands-off approach to managing investments.
How do target-date asset allocation funds differ from traditional investment funds?
Unlike traditional funds, target-date funds gradually shift towards a more conservative investment approach as the investor nears retirement age.
Are target-date asset allocation funds suitable for all investors?
While target-date funds offer convenience, investors should still assess their risk tolerance and financial goals before committing to this investment strategy.





