
How to adjust asset allocation for risk tolerance sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with a casual formal language style and brimming with originality from the outset.
Asset allocation plays a crucial role in managing investments, and understanding how to adjust it based on risk tolerance is key to optimizing returns and minimizing risks. This guide will delve into the intricacies of balancing risk and return to help you make informed decisions.
Introduction to Asset Allocation
Asset allocation is the process of dividing an investment portfolio among different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and cash equivalents. It is a crucial strategy for managing risk and achieving financial goals.
Importance of Asset Allocation for Risk Management
Asset allocation plays a vital role in managing risk because different asset classes tend to react differently to market conditions. By diversifying across asset classes, investors can reduce the impact of volatility on their overall portfolio.
- Diversification helps spread risk: By investing in a mix of assets, investors can reduce the impact of a downturn in any single asset class.
- Aligns with risk tolerance: Asset allocation allows investors to tailor their portfolios to their risk tolerance, ensuring they are comfortable with the level of risk they are taking.
- Optimizes returns: By balancing risk and return through asset allocation, investors can potentially achieve better long-term results.
Asset allocation is not about picking the best-performing assets, but about creating a well-balanced portfolio that aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
Examples of Asset Classes in Asset Allocation Strategies
Different asset classes commonly included in asset allocation strategies include:
- Stocks: Represent ownership in a company and offer the potential for high returns but also come with higher risk.
- Bonds: Debt securities issued by governments or corporations, providing regular interest payments and lower volatility compared to stocks.
- Cash Equivalents: Highly liquid, low-risk assets such as money market funds or certificates of deposit.
- Real Estate: Investments in physical properties or real estate investment trusts (REITs) for diversification and potential income.
Assessing Risk Tolerance
When it comes to making asset allocation decisions, understanding your risk tolerance is crucial. Risk tolerance refers to your ability and willingness to endure fluctuations in the value of your investments over time.
Factors Influencing Risk Tolerance
Several factors play a role in determining an individual’s risk tolerance:
- Time Horizon: The length of time you have to invest can impact your risk tolerance. Generally, the longer your time horizon, the more risk you can afford to take.
- Financial Goals: Your financial objectives and goals will influence how much risk you are willing to accept in your investments.
- Personality: Some individuals are naturally risk-averse, while others are more comfortable with taking risks.
- Income and Wealth: Your current financial situation, including income and existing wealth, can affect your risk tolerance.
Methods for Assessing Risk Tolerance
There are a few common methods to help you determine your risk tolerance level:
- Questionnaires: Many financial institutions offer risk tolerance questionnaires that can help assess your comfort level with risk.
- Professional Advice: Consulting with a financial advisor can provide insights into your risk tolerance based on your financial situation and goals.
- Self-Reflection: Reflecting on past investment experiences and how you reacted to market fluctuations can give you an idea of your risk tolerance.
Strategies for Adjusting Asset Allocation
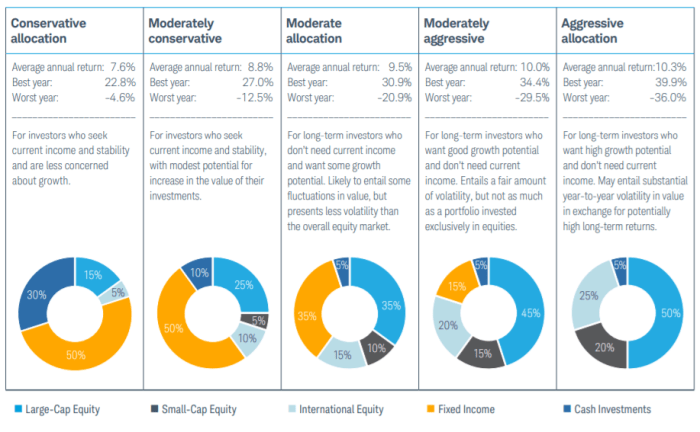
When it comes to adjusting asset allocation, it is crucial to consider an individual’s risk tolerance. Asset allocation is directly related to risk tolerance, as it determines the percentage of different asset classes in an investment portfolio based on an individual’s comfort level with risk.
One key concept in adjusting asset allocation is balancing risk and return. This means finding the right mix of investments that can potentially provide a desired level of return while managing the associated risks. It involves diversifying the portfolio across various asset classes to reduce the impact of market volatility on overall performance.
Adjusting Asset Allocation based on Varying Risk Tolerances
- Conservative Risk Tolerance: For individuals with a conservative risk tolerance, a larger portion of the portfolio may be allocated to low-risk investments such as bonds and cash equivalents. This helps minimize the impact of market fluctuations and provides stability to the portfolio.
- Moderate Risk Tolerance: Investors with a moderate risk tolerance may have a balanced allocation between equities and fixed-income securities. This allows for moderate growth potential while still providing some level of downside protection.
- Aggressive Risk Tolerance: Those with an aggressive risk tolerance may have a higher allocation to equities and alternative investments. While this approach comes with higher volatility, it also offers the potential for greater returns over the long term.
Implementing Changes in Asset Allocation
Adjusting asset allocation to align with changes in risk tolerance involves a systematic approach to ensure the portfolio remains in line with the investor’s goals and risk appetite.
Role of Diversification in Managing Risk
Diversification plays a crucial role in managing risk within a portfolio by spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, and regions. This helps reduce the impact of volatility in any single investment on the overall portfolio.
Steps in Adjusting Asset Allocation
- Assess Current Portfolio: Begin by reviewing the current holdings and their respective weights in the portfolio.
- Evaluate Risk Tolerance: Understand the investor’s risk tolerance and investment goals to determine the desired asset allocation mix.
- Identify Necessary Changes: Based on the assessment, identify areas where adjustments need to be made to align with the investor’s risk tolerance.
- Implement Changes: Rebalance the portfolio by buying or selling assets to achieve the desired asset allocation mix.
- Monitor and Review: Regularly monitor the portfolio’s performance and make adjustments as needed to maintain the desired risk level.
Monitoring and Reviewing Asset Allocation

Regularly monitoring and reviewing asset allocation is crucial to ensure that your investment portfolio remains aligned with your financial goals and risk tolerance. By staying vigilant and making necessary adjustments over time, you can optimize your asset allocation strategy for better long-term performance.
Importance of Regular Monitoring
Monitoring asset allocation on a regular basis allows you to track the performance of your investments and ensure that they are still in line with your risk tolerance and investment objectives. It also helps you identify any deviations from your target allocation and take timely actions to rebalance your portfolio.
Indicators for Adjustment
- Market Conditions: Changes in the market environment, such as economic fluctuations or geopolitical events, may impact the performance of different asset classes and warrant a reassessment of your allocation.
- Life Events: Significant life events like marriage, starting a family, or nearing retirement may require adjustments to your asset allocation to match your evolving financial needs and goals.
- Portfolio Performance: Poor performance of certain assets or sectors compared to others may signal the need to reallocate your investments for better diversification and risk management.
Tips for Optimization
- Stay Informed: Keep yourself updated on market trends, economic indicators, and investment news to make informed decisions about your asset allocation.
- Review Regularly: Set a schedule for reviewing your portfolio at least once a year or more frequently if there are significant changes in your financial situation or the market.
- Consult a Financial Advisor: Seeking guidance from a professional financial advisor can help you navigate complex investment decisions and ensure that your asset allocation aligns with your goals.
Asset Management vs. Asset Allocation
Asset management and asset allocation are two crucial components of a successful investment strategy. While they are closely related, they serve different purposes in achieving financial goals.
Definition and Relationship
Asset management involves the professional management of investments on behalf of clients. This includes buying, selling, and monitoring investments to optimize returns while managing risk. On the other hand, asset allocation refers to the strategic distribution of investments across different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and cash equivalents to achieve a balance between risk and return.
Differentiation in Investment Strategies
Asset management focuses on the day-to-day decisions of buying and selling securities within a portfolio. It aims to maximize returns based on market conditions and individual investment goals. Asset managers use their expertise to make informed decisions that align with the client’s objectives. On the other hand, asset allocation is a broader strategy that determines the overall mix of assets in a portfolio.
It considers factors such as risk tolerance, investment timeline, and financial goals to create a diversified portfolio. Asset allocation aims to reduce risk through spreading investments across different asset classes.
Complementary Relationship
Asset management and asset allocation work hand in hand to achieve financial goals. Asset managers rely on the asset allocation strategy to guide their investment decisions. By understanding the client’s risk tolerance and investment objectives set through asset allocation, asset managers can make informed decisions to optimize returns while managing risk effectively. In essence, asset management complements asset allocation by executing the investment strategy Artikeld in the asset allocation plan.
It involves the day-to-day management of investments to ensure they align with the overall goals and risk profile of the investor.
In conclusion, mastering the art of adjusting asset allocation for risk tolerance is a vital skill for any investor looking to navigate the complex world of finance. By carefully managing your asset mix in line with your risk appetite, you can enhance your investment portfolio’s performance and achieve your financial goals with confidence.
General Inquiries
How often should I review my asset allocation?
You should review your asset allocation at least once a year or whenever there are significant changes in your financial situation.
Can asset allocation help reduce investment risk?
Yes, by diversifying your investments across different asset classes, you can reduce the overall risk in your portfolio.
Is it necessary to adjust asset allocation based on changing risk tolerance?
Yes, it is crucial to adjust your asset allocation to align with your risk tolerance as your financial goals or circumstances change.





